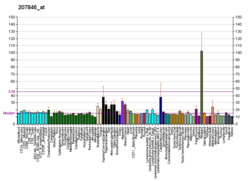
Pituitary-specific positive transcription factor 1
POU domain, class 1, transcription factor 1 (Pit1, growth hormone factor 1), also known as POU1F1, is a transcription factor for growth hormone.[5]
Function
PIT1 is a pituitary-specific transcription factor responsible for pituitary development and hormone expression in mammals and is a member of the POU family of transcription factors that regulate mammalian development. The POU family is so named because the first 3 members identified were PIT1 and OCT1 (MIM 164175) of mammals, and Unc-86 of C. elegans (Herr et al., 1988). PIT1 contains 2 protein domains, termed POU-specific and POU-homeo, which are both necessary for high affinity DNA binding on genes encoding growth hormone (GH; MIM 139250) and prolactin (PRL; MIM 176760). PIT1 is also important for regulation of the genes encoding prolactin and thyroid-stimulating hormone beta subunit (TSHB; MIM 188540) by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH; MIM 257120) and cyclic AMP.[supplied by OMIM][5]
Interactions
Pituitary-specific positive transcription factor 1 has been shown to interact with GATA2[6] and PITX1.[7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000064835 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000004842 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: POU1F1 POU domain, class 1, transcription factor 1 (Pit1, growth hormone factor 1)".
- ^ Dasen JS, O'Connell SM, Flynn SE, Treier M, Gleiberman AS, Szeto DP, Hooshmand F, Aggarwal AK, Rosenfeld MG (May 1999). "Reciprocal interactions of Pit1 and GATA2 mediate signaling gradient-induced determination of pituitary cell types". Cell. 97 (5): 587–98. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80770-9. PMID 10367888. S2CID 15737684.
- ^ Szeto DP, Ryan AK, O'Connell SM, Rosenfeld MG (July 1996). "P-OTX: a PIT-1-interacting homeodomain factor expressed during anterior pituitary gland development". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (15): 7706–10. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.15.7706. PMC 38811. PMID 8755540.
Further reading
- Parks JS, Brown MR (1999). "Transcription factors regulating pituitary development". Growth Horm. IGF Res. 9 Suppl B: 2–8, discussion 8–11. doi:10.1016/S1096-6374(99)80074-4. PMID 10549299.
- Rodriguez R, Andersen B (2003). "Cellular determination in the anterior pituitary gland: PIT-1 and PROP-1 mutations as causes of human combined pituitary hormone deficiency". Minerva Endocrinol. 28 (2): 123–33. PMID 12717343.
- Quentien MH, Barlier A, Franc JL, Pellegrini I, Brue T, Enjalbert A (2006). "Pituitary transcription factors: from congenital deficiencies to gene therapy". J. Neuroendocrinol. 18 (9): 633–42. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2006.01461.x. PMID 16879162. S2CID 21835164.
- Cattini PA, Yang X, Jin Y, Detillieux KA (2006). "Regulation of the human growth hormone gene family: possible role for Pit-1 in early stages of pituitary-specific expression and repression". Neuroendocrinology. 83 (3–4): 145–53. doi:10.1159/000095522. PMID 17047377. S2CID 34757447.
- Li X, Giachelli CM (2007). "Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters and vascular calcification". Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 16 (4): 325–8. doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e3281c55ef1. PMID 17565274. S2CID 25963053.
- Tatsumi K, Miyai K, Notomi T, Kaibe K, Amino N, Mizuno Y, Kohno H (1993). "Cretinism with combined hormone deficiency caused by a mutation in the PIT1 gene". Nat. Genet. 1 (1): 56–8. doi:10.1038/ng0492-56. PMID 1302000. S2CID 36138691.
- Tatsumi K, Notomi T, Amino N, Miyai K (1992). "Nucleotide sequence of the complementary DNA for human Pit-1/GHF-1". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1129 (2): 231–4. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(92)90494-k. PMID 1370379.
- Ohta K, Nobukuni Y, Mitsubuchi H, Fujimoto S, Matsuo N, Inagaki H, Endo F, Matsuda I (1993). "Mutations in the Pit-1 gene in children with combined pituitary hormone deficiency". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189 (2): 851–5. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)92281-2. PMID 1472057.
- Ohta K, Nobukuni Y, Mitsubuchi H, Ohta T, Tohma T, Jinno Y, Endo F, Matsuda I (1993). "Characterization of the gene encoding human pituitary-specific transcription factor, Pit-1". Gene. 122 (2): 387–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90234-G. PMID 1487156.
- Radovick S, Nations M, Du Y, Berg LA, Weintraub BD, Wondisford FE (1992). "A mutation in the POU-homeodomain of Pit-1 responsible for combined pituitary hormone deficiency". Science. 257 (5073): 1115–8. doi:10.1126/science.257.5073.1115. PMID 1509262. S2CID 33620091.
- Pfäffle RW, DiMattia GE, Parks JS, Brown MR, Wit JM, Jansen M, Van der Nat H, Van den Brande JL, Rosenfeld MG, Ingraham HA (1992). "Mutation of the POU-specific domain of Pit-1 and hypopituitarism without pituitary hypoplasia". Science. 257 (5073): 1118–21. doi:10.1126/science.257.5073.1118. PMID 1509263. S2CID 32400112.
- Lew AM, Elsholtz HP (1991). "Cloning of the human cDNA for transcription factor Pit-1". Nucleic Acids Res. 19 (22): 6329. doi:10.1093/nar/19.22.6329. PMC 329149. PMID 1956794.
- He X, Treacy MN, Simmons DM, Ingraham HA, Swanson LW, Rosenfeld MG (1989). "Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development". Nature. 340 (6228): 35–41. doi:10.1038/340035a0. PMID 2739723. S2CID 4275887.
- Bodner M, Castrillo JL, Theill LE, Deerinck T, Ellisman M, Karin M (1988). "The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein". Cell. 55 (3): 505–18. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. PMID 2902927. S2CID 26376487.
- Herr W, Sturm RA, Clerc RG, Corcoran LM, Baltimore D, Sharp PA, Ingraham HA, Rosenfeld MG, Finney M, Ruvkun G (1989). "The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products". Genes Dev. 2 (12A): 1513–6. doi:10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. PMID 3215510.
- de Zegher F, Pernasetti F, Vanhole C, Devlieger H, Van den Berghe G, Martial JA (1995). "The prenatal role of thyroid hormone evidenced by fetomaternal Pit-1 deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80 (11): 3127–30. doi:10.1210/jc.80.11.3127. PMID 7593413.
- Bamberger AM, Bamberger CM, Pu LP, Puy LA, Loh YP, Asa SL (1995). "Expression of pit-1 messenger ribonucleic acid and protein in the human placenta". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80 (7): 2021–6. doi:10.1210/jc.80.7.2021. PMID 7608249.
- Irie Y, Tatsumi K, Ogawa M, Kamijo T, Preeyasombat C, Suprasongsin C, Amino N (1995). "A novel E250X mutation of the PIT1 gene in a patient with combined pituitary hormone deficiency". Endocr. J. 42 (3): 351–4. doi:10.1507/endocrj.42.351. PMID 7670563.
- Delhase M, Vila V, Hooghe-Peters EL, Castrillo JL (1995). "A novel pituitary transcription factor is produced by alternative splicing of the human GHF-1/PIT-1 gene". Gene. 155 (2): 273–5. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)00757-J. PMID 7721104.
- Okamoto N, Wada Y, Ida S, Koga R, Ozono K, Chiyo H, Hayashi A, Tatsumi K (1995). "Monoallelic expression of normal mRNA in the PIT1 mutation heterozygotes with normal phenotype and biallelic expression in the abnormal phenotype". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (9): 1565–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.9.1565. PMID 7833912.
External links
- PIT1+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Transcription+Factor+Pit-1 at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)