bZIP domain
| bZIP transcription factor | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
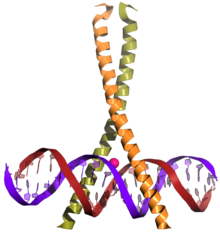 CREB (top) is a transcription factor capable of binding DNA via the bZIP domain (bottom) and regulating gene expression. | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | bZIP_1 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00170 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011616 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00036 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1ysa / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| CDD | cd14686 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (bZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors.[1][2]
bZIP transcription factors
bZIP transcription factors are found in all organisms. A recent evolutionary study revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded by the genome of the most recent common ancestor of all plants.[3] Interactions between bZIP transcription factors play important roles in cancer development[4] in epithelial tissues, steroid hormone synthesis by cells of endocrine tissues,[5] factors affecting reproductive functions,[6] and several other phenomena that affect human health.
bZIP domain containing proteins
- AP-1 fos/jun heterodimer that forms a transcription factor
- Jun-B transcription factor
- CREB cAMP response element transcription factor
- OPAQUE2 (O2) transcription factor of the 22-kD zein gene that encodes a class of storage proteins in the endosperm of maize (Zea Mays) kernels
- NFE2L2 or Nrf2
- Bzip Maf transcription factors
Human proteins containing this domain
ATF1; ATF2; ATF4; ATF5; ATF6; ATF7; BACH1; BACH2; BATF; BATF2; CREB1; CREB3; CREB3L1; CREB3L2; CREB3L3; CREB3L4; CREB5; CREBL1; CREM; E4BP4; FOSL1; FOSL2; JUN; JUNB; JUND; MAFA; MAFB; NFE2; NFE2L2; NFE2L3; SNFT; XBP1
External links
- bZIP domain entry in the SMART database
- bZIP family at PlantTFDB: Plant Transcription Factor Database
- Plant bZIP transcription factors
References
- ^ Ellenberger T (1994). "Getting a grip in DNA recognition: structures of the basic region leucine zipper, and the basic region helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domains". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4 (1): 12–21. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(94)90054-X.
- ^ Hurst HC (1995). "Transcription factors 1: bZIP proteins". Protein Profile. 2 (2): 101–68. PMID 7780801.
- ^ Corrêa LGG, Riaño-Pachón DM, Schrago CG, dos Santos RV, Mueller-Roeber B, Vincentz M. (2008). Shiu, Shin-Han (ed.). "The Role of bZIP Transcription Factors in Green Plant Evolution: Adaptive Features Emerging from Four Founder Genes". PLoS ONE. 3 (8): e2944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002944. PMC 2492810. PMID 18698409.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Vlahopoulos SA, Logotheti S, Mikas D, Giarika A, Gorgoulis V, Zoumpourlis V (April 2008). "The role of ATF-2 in oncogenesis". BioEssays. 30 (4): 314–27. doi:10.1002/bies.20734. PMID 18348191.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Manna PR, Dyson MT, Eubank DW, Clark BJ, Lalli E, Sassone-Corsi P, Zeleznik AJ, Stocco DM (January 2002). "Regulation of steroidogenesis and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by a member of the cAMP response-element binding protein family". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (1): 184–99. doi:10.1210/me.16.1.184. PMID 11773448.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hoare S, Copland JA, Wood TG, Jeng YJ, Izban MG, Soloff MS (May 1999). "Identification of a GABP alpha/beta binding site involved in the induction of oxytocin receptor gene expression in human breast cells, potentiation by c-Fos/c-Jun". Endocrinology. 140 (5): 2268–79. doi:10.1210/en.140.5.2268. PMID 10218980.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
